Visual SLAM with RBG-D camera for navigation
Intro
This project is part of the Autonomoues Robotics course at UTEC. The objective of this project is to compare maps obtained through ViSLAM using RTABMap with stereo camera configuration and the use of an RGB-D depth camera.
Here, we area evaluating both approaches with the Turtlebot3 Waffle Pi robot. Also, we are using the following map to evaluate the obtained results with the ground truth.

Metodology
A. Navigation Algorithm with 2D Lidar
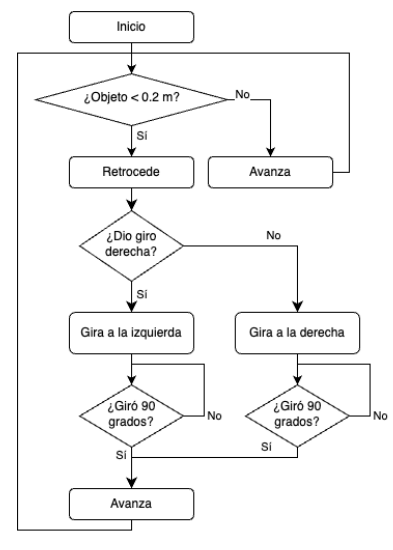
The first step of the methodology is to establish a navigation algorithm based on the measurements that performs 2D LiDAR. The flow chart of this algorithm is detailed better in the figure below. The essence is to avoid collision with obstacles while navigating through an unknown environment performing the SLAM.
B. Visual SLAM - Stereo Camera
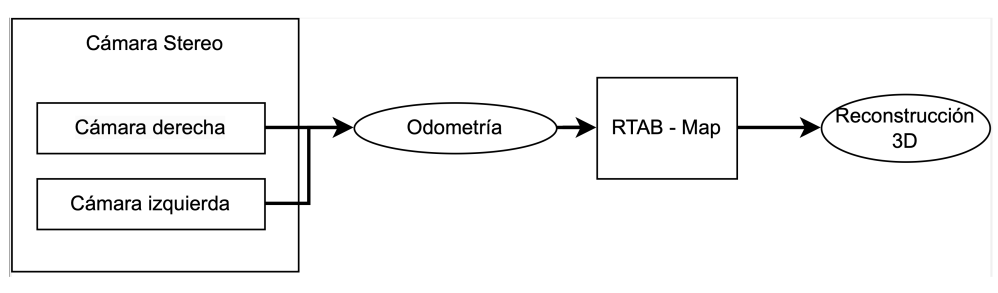
To make localization and mapping for the robot. The first method to obtain the map of the environment is to use two cameras in stereo configuration. That is the reason to first calibrate the cameras with an chess board in Gazebo (You can refer to the Camera Calibration in Gazebo). The input will be the two images of the cameras (left and right) to obtain the cloud point from the robot frame and then, we use the R-TabMap library to convert these cloudpoints into a map. We will be use the following logic shown in the figure below.
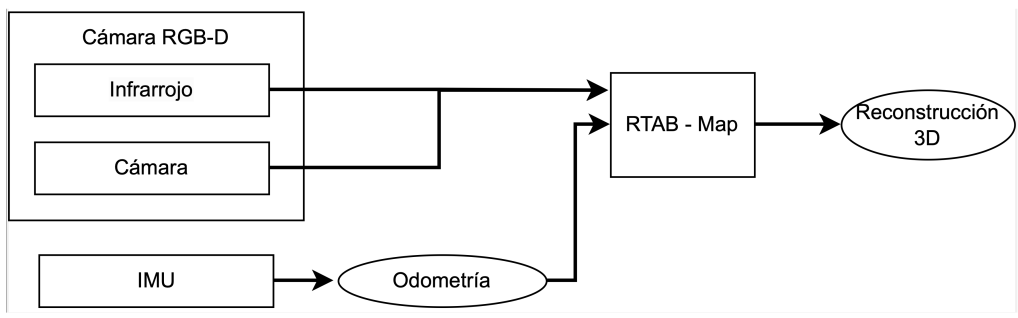
C. Visual SLAM - Kinect + IMU
This second method consists on the usage of a depth camera (Kinect) and the IMU for robot’s pose estimation. In this case, we will be using the same library as in B, so it needs the odometry and the pointcloud. For the odometry, we are going to apply Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) for pose estimation having linear acceleration and angular velocity as measurements.
Simulation
The neccesary packages to run the project are described in thebelow.
1. Creating a directory for turtlebots files.
cd src
mkdir turtlebot3
cd turtlebot3
git clone -b noetic-devel https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3.git
git clone -b noetic-devel https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_msgs.git
git clone -b noetic-devel https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_simulations.git
2. Cloning the repository of the project.
cd ..
git clone https://github.com/Jimi1811/Visual_SLAM_in_turtlebot3.git
cd ..
catkin_make
3. Cloning additional packages that helps the camera calibration.
cd src
git clone https://github.com/ros-perception/image_pipeline.git
cd ..
catkin_make --only-pkg-with-deps stereo_image_proc
4. Running these lines below to execute the SLAM simulation.
roslaunch stereo_camera maze.launch
ROS_NAMESPACE=/stereo rosrun stereo_image_proc stereo_image_proc
roslaunch rtabmap_legacy stereo_mapping.launch stereo_namespace:="/stereo" rtabmap_args:="--delete_db_on_start" rviz:=true rtabmapviz:=false
The following image describes the world we are trying to mrun the SLAM algorithm with the turtlebot3.

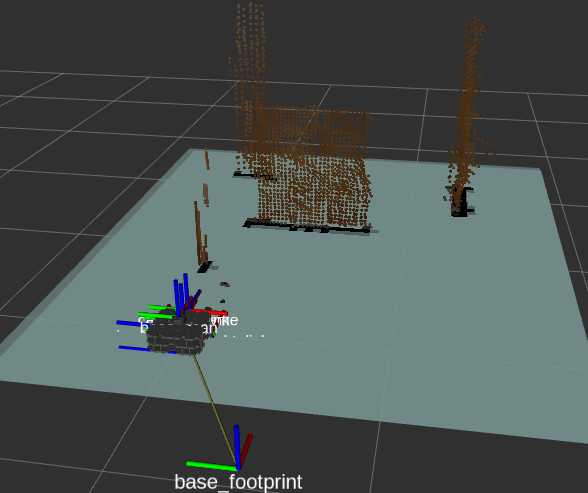
The voxels (little cubes in rviz) compound the pointcloud, which will be an input for the R-TabMap. This refers to the first method (stereo camera)
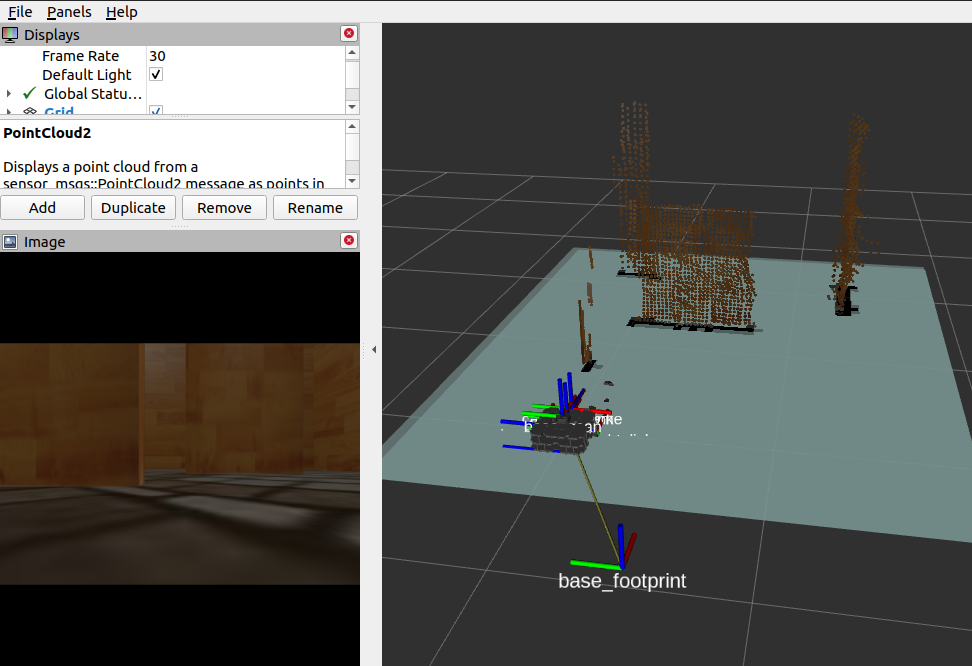
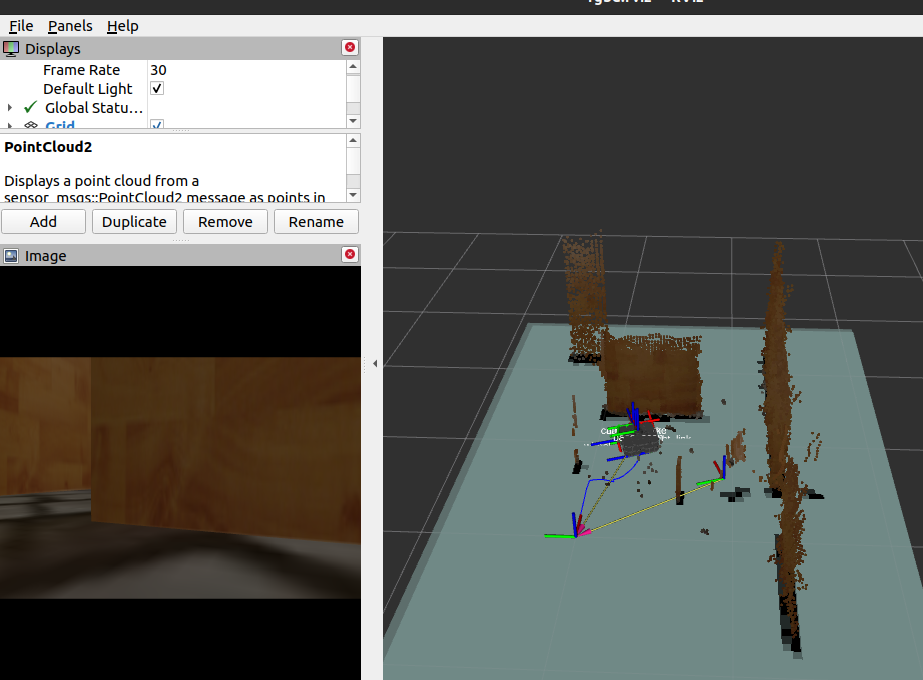
Here it is the turtlebot exploring new positions and poses inside the environment. While it is moving, the pointclouds try to match to make up the map.
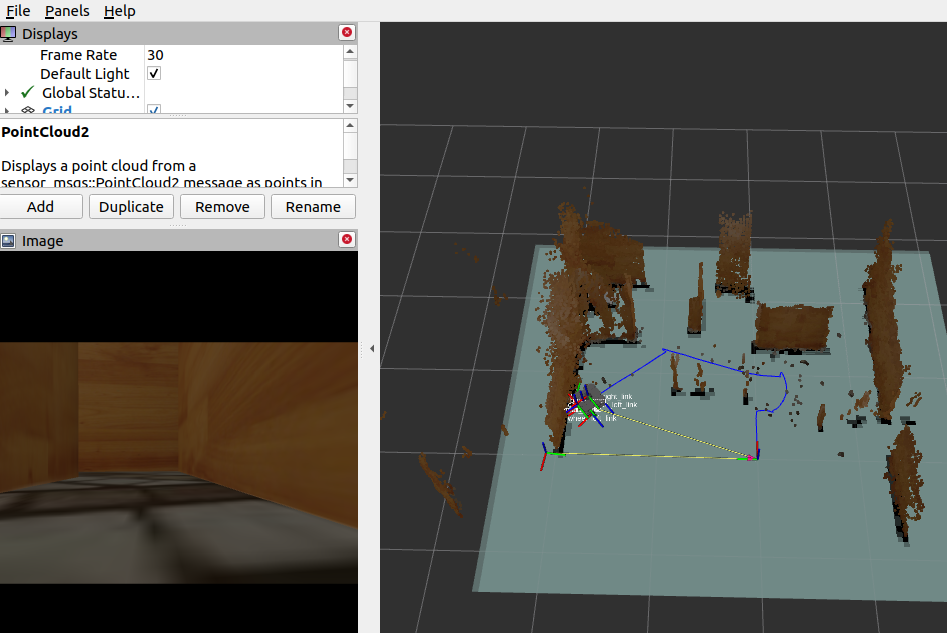
Finally, it is seen that when trying to move the turtlebot for too long, it may cause some displacement between its real position and the one received in Rviz, causing an incorrect mapping.
Results
Now, it is important to measure how accurate are the methods shown previously. That is the reason we will be comparing the grid map obtained by the algorithms to its ground truth. We will use two measurements to compare which one of both is better. (correlation and minimun square error).
The next image corresponds to the stereo method
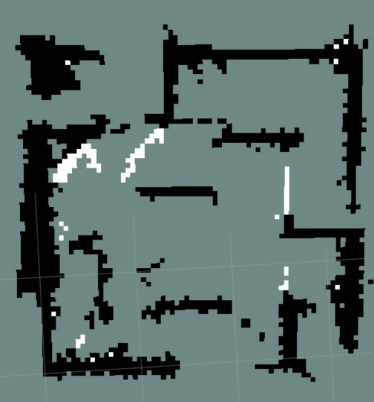
This map is the result of the second method.

| |RGB-D & EKF | | Stereo Vision| | |
|---|---|---|
| Correlación | 0.189 | 0.2157 |
| MSE | 0.7104 | 0.808 |
Both SLAM methods, using RGB-D camera and stereo vision, they managed to successfully complete the task of mapping of the proposed map. However, each method has its limitations. The RGB-D method has restrictions on regarding distance, since its detection range is limited. On the other hand, the stereo vision method requires super- fices with textures and can be affected by conditions of lighting. As recommendations, it is suggested to improve the navigation algorithm to avoid collisions and optimize the filters used for the IMU, in order to obtain a more accurate estimation of the robot pose. These improvements will contribute to obtaining more robust and reliable results in future 3D mapping applications with Visual SLAM.
Here it is an article about this project (Spanish):
The code can be located here.